Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) hijacking is a form of cyber attack that threatens the very foundations of the internet. It exploits a chief component that manages how data is routed across the vast network of internet-connected devices.
Table of Contents
Understanding BGP
Before we dive into the intricacies of a BGP hijack, it’s essential to understand what BGP is and why it plays such a crucial role in online communication. Broadly speaking, the Border Gateway Protocol is a routing protocol used to exchange routing information among the networks on the internet. It decides which path data takes to reach its destination, and thus essentially builds the roadmaps for internet data transmissions.
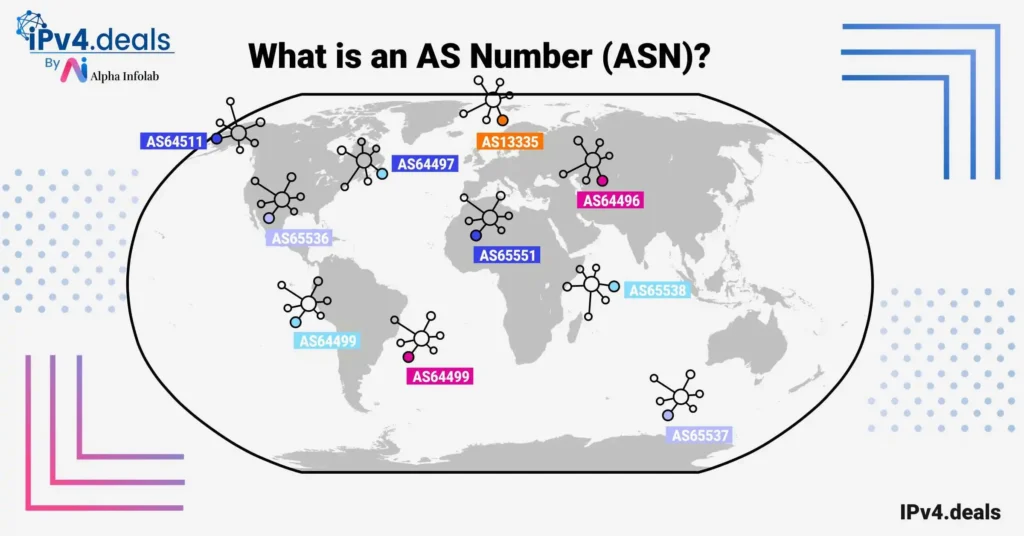
BGP enables networks, also known as Autonomous Systems (AS), to communicate with each other, sharing data about their reachability. As an example, if a user in Japan wants to open a web page hosted on a server in Germany, BGP determines the best route for the data to travel. Under normal conditions, BGP is efficient and reliable. However, the protocol was built during the early days of the internet, and security was not seen as a primary concern at that time. As a result, the BGP system trusts the data it receives from other systems to be correct, making it vulnerable to malicious manipulation.
Understanding hijacking
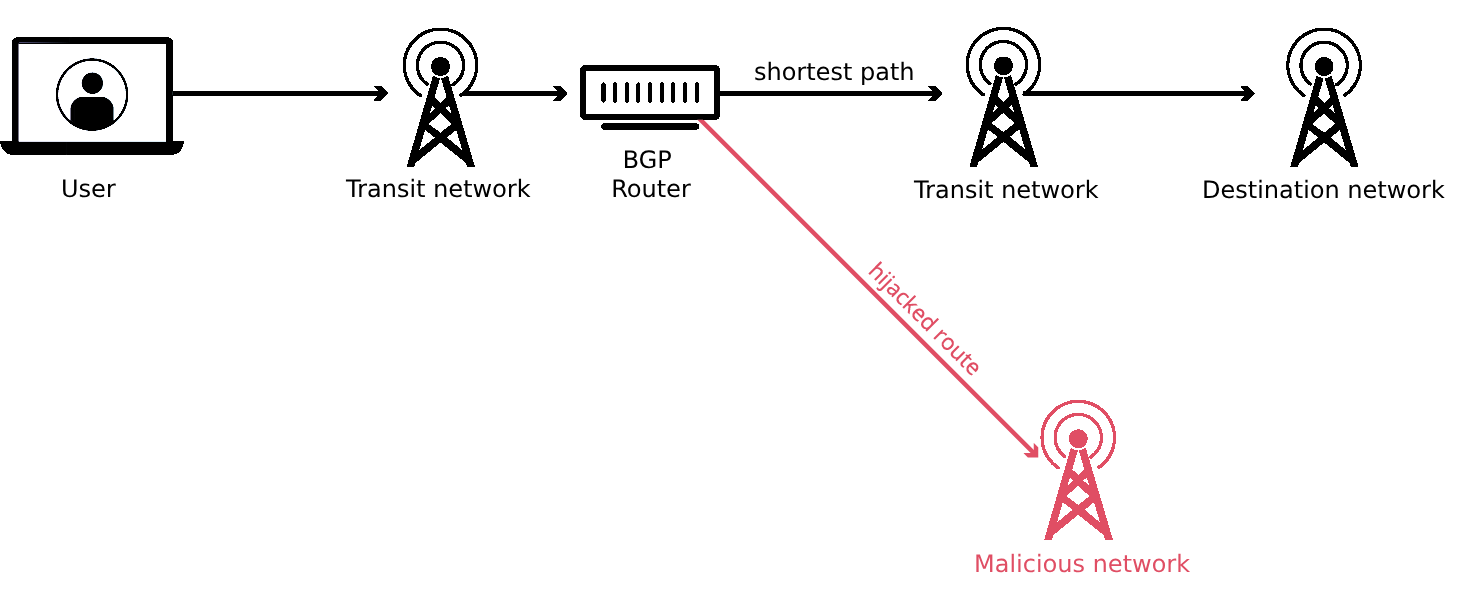
This vulnerability is where BGP hijacking comes into play. In this form of attack, a malicious actor misdirects internet traffic by falsely claiming to own an IP address range in the BGP system. By broadcasting ‘false’ routing information, the attacker can reroute traffic intended for a specific IP address range to their own network.
Delving deeper into the mechanics of a BGP hijack reveals the real danger behind this attack form. For instance, the attacker might reroute traffic to collect sensitive data, effect a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack, or carry out large-scale internet censorship. Let’s take a hypothetical example of a user trying to log into their bank account. If the bank’s network is the target of a BGP hijack, when the user enters their login credentials, they could be redirected to a fake site controlled by the attacker, who can then harvest the user’s credentials. Alternatively, the attacker could simply stop the traffic from reaching its intended destination, leading to a DoS condition.
BGP hijacking can be challenging to detect because, in many cases, the users don’t even realize that they’ve been redirected. More concerning is the fact that these attacks can also be difficult to prevent due to the reliance of BGP on mutual trust between systems. However, there have been efforts to increase the resilience of the BGP system.
Security Measures
One such effort is the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI). RPKI uses cryptographic validation to ensure that routing data comes from the legitimate owner of an IP address block, therefore enhancing the security of BGP. Other potential solutions involve inherently making BGP more secure through path-end validation and ensuring transparency in routing changes.
In conclusion, BGP hijacking poses a substantial threat to the internet as it stands today because of the inherent weaknesses in the protocol. While there are solutions available and in development to increase the security of the BGP system, it will take considerable coordinated effort from the vast number of networks that make up the internet to implement these effectively. Until then, the internet will remain vulnerable to BGP hijacks, emphasizing the ongoing need for robust cybersecurity infrastructure and practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is BGP hijacking?
BGP hijacking is a form of cyber attack that exploits the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to misdirect internet traffic by falsely claiming to own an IP address range.
What role does BGP play in internet communication?
BGP is a routing protocol used to exchange routing information among networks on the internet. It determines the path data takes to reach its destination, essentially creating roadmaps for internet data transmissions.
What are Autonomous Systems (AS) in the context of BGP?
Autonomous Systems (AS) are networks that communicate with each other using BGP, sharing data about their reachability on the internet.
Why is BGP vulnerable to hijacking?
BGP was developed during the early days of the Internet when security was not a primary concern. As a result, BGP inherently trusts the data it receives from other systems, making it susceptible to malicious manipulation.
How does a BGP hijacking attack work?
In a BGP hijacking attack, a malicious actor broadcasts false routing information, claiming to own a specific IP address range. This causes internet traffic intended for that IP range to be rerouted to the attacker’s network.
What are the potential consequences of a BGP hijack?
Attackers can reroute traffic to collect sensitive data, execute a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack, or implement large-scale internet censorship. For example, users could be redirected to fake sites to harvest login credentials.
Why is BGP hijacking hard to detect?
BGP hijacking can be challenging to detect because users often don’t realize they’ve been redirected. The attack exploits the mutual trust between systems in the BGP protocol.
What is the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI)?
RPKI is a security measure that uses cryptographic validation to ensure routing data originates from the legitimate owner of an IP address block, enhancing BGP security.
Are there other solutions to enhance BGP security?
Yes, other potential solutions include making BGP inherently more secure through path-end validation and ensuring transparency in routing changes.
How significant is the threat of BGP hijacking to the current internet?
BGP hijacking poses a substantial threat due to inherent weaknesses in the protocol. While solutions are available and in development, coordinated efforts are required to implement these effectively, emphasizing the need for robust cybersecurity practices.
How can I protect my IPv4 network from security threats?
Use VPNs, install firewalls, and keep your system updated to secure your IPv4 network. Learn more about IPv4 Security: Best Practices and Vulnerabilities.