Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) acts as the internet’s routing system, determining the most efficient path for data to travel from its source to its destination. Imagine needing to send a letter from New York to Los Angeles; BGP is like the system that decides whether the letter should go directly or make stops along the way. By connecting networks managed by different organizations, known as Autonomous Systems (AS), BGP keeps the internet functional and efficient. In this exploration, we’ll delve into how BGP operates, its key features, the challenges it faces, and the measures taken to secure its operations.
Table of Contents
BGP Basics
Path Vector Protocol
BGP, a Path Vector Protocol, maintains the path information that dynamically changes to ensure data finds the most efficient route, avoiding loops in the network.
Autonomous Systems (AS)
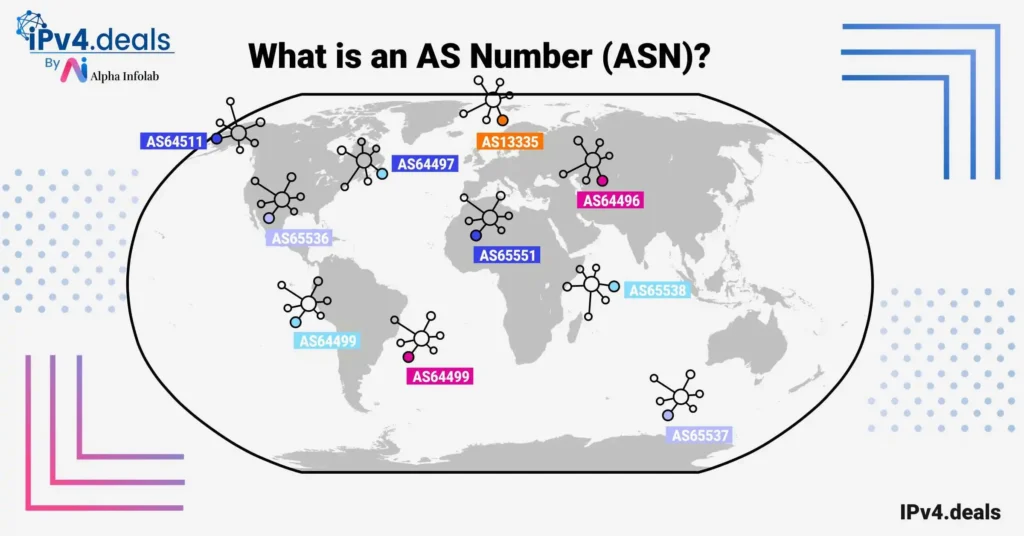
Autonomous Systems (AS) are networks under a single organization’s control, each with a unique identifier. BGP facilitates the exchange of routing information between these ASes, enabling the broader internet connectivity we experience.
Operational Simplicity
In a simplified scenario, suppose there are only six ASes on the internet. If AS1 needs to route a packet to AS3, it has options:
- Hopping to AS2 and then to AS3: AS1 → AS2 → AS3
- Or hopping to AS6, then to AS5, AS4, and finally to AS3: AS1 → AS6 → AS5 → AS4 → AS3
The decision seems straightforward with fewer hops being quicker. However, in reality, with hundreds of thousands of ASes and various factors at play, BGP’s complex route selection algorithm ensures the most efficient route is chosen, showcasing the protocol’s operational intricacy balanced with simplicity.
Key Features
Route Aggregation
BGP can simplify routing by grouping multiple IP network routes together into a single summarized route. This helps in reducing the amount of routing information that needs to be exchanged and processed, making the network more manageable.
Path Attributes
BGP uses certain parameters, known as path attributes, to decide which path to take to reach a destination. These parameters include information like the next-hop IP address and the path’s preference value. By evaluating these attributes, BGP can determine the most efficient route for data transmission.
Policy-Based Routing
BGP allows network administrators to set rules for routing. These rules, set based on organizational needs and preferences, guide how routing decisions are made. This feature provides a level of control over routing behavior, helping to align network operations with organizational objectives.
Security Concerns
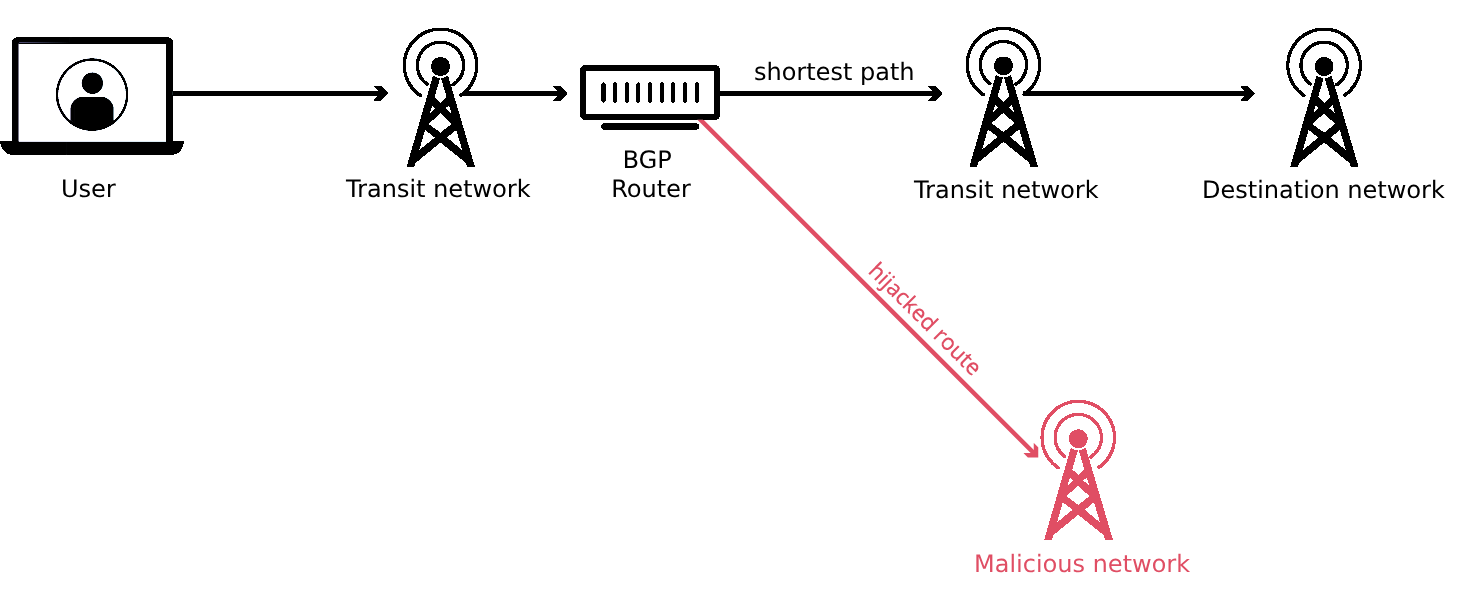
BGP’s open nature, which allows for the wide exchange of routing information, can also be a source of security issues. One such issue is BGP hijacking, where unauthorized entities can misdirect traffic through their own networks, potentially for malicious purposes. Addressing these security challenges is an ongoing effort, requiring the internet community to develop and implement measures that enhance BGP’s security and ensure the reliable routing of data.
Various incidents highlight the vulnerabilities in BGP. For instance, a Turkish ISP, TTNet, in 2004 mistakenly advertised incorrect BGP routes, causing a massive disruption. In 2008, a Pakistani ISP’s attempt to block YouTube led to a global accessibility issue for the platform. In 2019, a small company in Pennsylvania inadvertently became a preferred path for routes through Verizon’s network, causing internet outages. These incidents underscore the need for enhanced security measures in BGP to prevent both accidental and deliberate misrouting of internet traffic.
To mitigate hijacking risks, the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) was introduced in 2008. RPKI uses cryptographically signed records to validate network operators authorized to announce an organization’s IP addresses using BGP. While more than half of top internet providers support RPKI, broader adoption is needed to fully secure BGP. Implementing RPKI and network alerting technologies can significantly contribute to preventing BGP hijacking attacks.
External BGP and Internal BGP
External BGP (eBGP) facilitates the exchange of routing information between different ASes on the internet, while Internal BGP (iBGP) operates within an AS. Unlike eBGP, iBGP is not a requirement for routing within an AS, as other protocols can be used.
Recap
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) holds a critical role in guiding data across the internet’s vast network of interconnected systems. Through its unique operational mechanisms and the ability to efficiently manage routing information among different networks, BGP ensures that data reaches its intended destination reliably. While it faces security challenges like BGP hijacking, the continuous efforts to enhance its security measures show the internet community’s commitment to maintaining a robust and reliable global network.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)?
BGP is the internet’s routing system, determining the most efficient path for data to travel from its source to its destination. It connects networks managed by different organizations, known as Autonomous Systems (AS), to keep the Internet functional and efficient.
What is an Autonomous System (AS)?
An Autonomous System (AS) is a network under a single organization’s control, each with a unique identifier. BGP facilitates the exchange of routing information between these ASes.
How does BGP’s Path Vector Protocol work?
BGP, as a Path Vector Protocol, maintains dynamic path information to ensure data finds the most efficient route, avoiding network loops.
What is Route Aggregation in BGP?
Route Aggregation in BGP groups multiple IP network routes into a single summarized route, reducing the amount of routing information exchanged and processed, making the network more manageable.
How does BGP decide which path to take?
BGP uses path attributes, such as the next-hop IP address and the path’s preference value, to determine the most efficient route for data transmission.
What is Policy-Based Routing in BGP?
Policy-based routing in BGP allows network administrators to set rules for routing based on organizational needs and preferences, providing control over routing behavior.
What are the security concerns associated with BGP?
BGP’s open nature can lead to security issues like BGP hijacking, where unauthorized entities misdirect traffic. Addressing these security challenges requires ongoing efforts to develop and implement security measures.
What is the difference between External BGP (eBGP) and Internal BGP (iBGP)?
eBGP facilitates the exchange of routing information between different ASes on the internet, while iBGP operates within an AS. iBGP is not a requirement for routing within an AS, as other protocols can be used.
What measures are being taken to enhance BGP’s security?
To mitigate hijacking risks, the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) was introduced in 2008. RPKI uses cryptographically signed records to validate network operators authorized to announce an organization’s IP addresses using BGP.
What role does BGP play in the internet’s functioning?
BGP plays a critical role in guiding data across the internet’s vast network of interconnected systems, ensuring that data reaches its intended destination reliably.
What is an Internet Exchange Point (IXP)?
An IXP is a physical infrastructure through which different Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and network operators connect their networks to exchange traffic with each other.